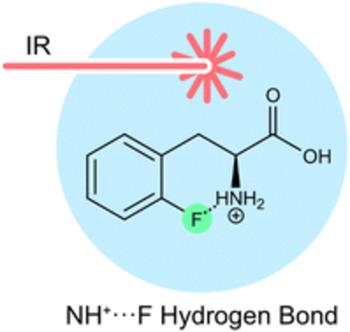
Cryogenic infrared spectroscopy reveals remarkably short NH+⋯F hydrogen bonds in fluorinated phenylalanines
Safferthal, M.; Greis, K.; Chang, R.; Kirschbaum, C.; Hoffmann, W.; Meijer, G.; von Helden, G.; Pagel, K.* – 2023
In past decades, hydrogen bonds involving organic fluorine have been a highly disputed topic. Obtaining clear evidence for the presence of fluorine-specific interactions is generally difficult because of their weak nature. Today, the existence of hydrogen bonds with organic fluorine is widely accepted and supported by numerous studies. However, strong bonds with short H⋯F distances remain scarce and are primarily found in designed model compounds. Using a combination of cryogenic gas-phase infrared spectroscopy and density functional theory, we here analyze a series of conformationally unrestrained fluorinated phenylalanine compounds as protonated species. The results suggest proximal NH+⋯F hydrogen bonds with an exceptionally close H⋯F distance (1.79 Å) in protonated ortho-fluorophenylalanine.
In past decades, hydrogen bonds involving organic fluorine have been a highly disputed topic. Obtaining clear evidence for the presence of fluorine-specific interactions is generally difficult because of their weak nature. Today, the existence of hydrogen bonds with organic fluorine is widely accepted and supported by numerous studies. However, strong bonds with short H⋯F distances remain scarce and are primarily found in designed model compounds. Using a combination of cryogenic gas-phase infrared spectroscopy and density functional theory, we here analyze a series of conformationally unrestrained fluorinated phenylalanine compounds as protonated species. The results suggest proximal NH+⋯F hydrogen bonds with an exceptionally close H⋯F distance (1.79 Å) in protonated ortho-fluorophenylalanine.