Cryogenic infrared spectroscopy provides mechanistic insight into the fragmentation of phospholipid silver adducts
Kirschbaum, C.; Greis, K.; Gewinner, S.; Schöllkopf, W.; Meijer, G.; von Helden, G.; Pagel, K.* – 2022
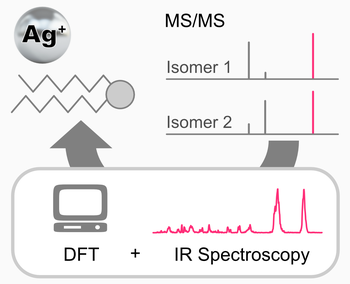
Tandem mass spectrometry is arguably the most important analytical tool for structure elucidation of lipids and other metabolites. By fragmenting intact lipid ions, valuable structural information such as the lipid class and fatty acyl composition are readily obtainable. The information content of a fragment spectrum can often be increased by the addition of metal cations. In particular, the use of silver ions is deeply rooted in the history of lipidomics due to their propensity to coordinate both electron-rich heteroatoms and C = C bonds in aliphatic chains. Not surprisingly, coordination of silver ions was found to enable the distinction of sn-isomers in glycerolipids by inducing reproducible intensity differences in the fragment spectra, which could, however, not be rationalized. Here, we investigate the fragmentation behaviors of silver-adducted sn- and double bond glycerophospholipid isomers by probing fragment structures using cryogenic gas-phase infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Our results confirm that neutral headgroup loss from silver-adducted glycerophospholipids leads to dioxolane-type fragments generated by intramolecular cyclization. By combining high-resolution IR spectroscopy and computational modelling of silver-adducted fragments, we offer qualitative explanations for different fragmentation behaviors of glycerophospholipid isomers. Overall, the results demonstrate that gas-phase IR spectroscopy of fragment ions can significantly contribute to our understanding of lipid dissociation mechanisms and the influence of coordinating cations.