Excavating Hidden Adsorption Sites in Metal-Organic Frameworks Using Rational Defect Engineering
S. Chong, G. Thiele, J. Kim – 2018
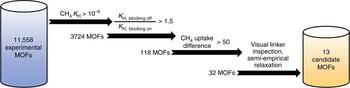
Metal–organic frameworks are known to contain defects within their crystalline structures. Successful engineering of these defects can lead to modifications in material properties that can potentially improve the performance of many existing frameworks. Herein, we report the high-throughput computational screening of a large experimental metal–organic framework database to identify 13 frameworks that show significantly improved methane storage capacities with linker vacancy defects. The candidates are first identified by focusing on structures with methane-inaccessible pores blocked away from the main adsorption chan- nels. Then, organic linkers of the candidate structures are judiciously replaced with appro- priate modulators to emulate the presence of linker vacancies, resulting in the integration and utilization of the previously inaccessible pores. Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations of defective candidate frameworks show significant enhancements in methane storage capa- cities, highlighting that rational defect engineering can be an effective method to significantly improve the performance of the existing metal–organic frameworks.