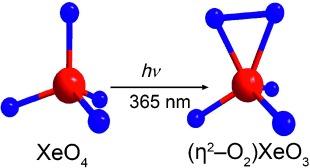
Ultraviolet Photolysis Studies on XeO4 in Noble-Gas and F2 Matrices and the Formation and Characterization of a New XeVIII Oxide, (η2-O2)XeO3
Thomas Vent-Schmidt, James T. Goettel, Gary J. Schrobilgen, Sebastian Riedel – 2015
The photolytic behavior of the thermochemically unstable xenon(VIII) oxide XeO₄ was investigated by UV irradiation in noble‐gas and F₂ matrices. Photolysis of Xe¹⁶O₄ or Xe¹⁸O₄ in noble‐gas matrices at 365 nm yielded XeO₃ and a new xenon(VIII) oxide, namely, (η²‐O₂)XeO₃, which, along with XeO₄, was characterized by matrix‐isolation IR spectroscopy and quantum‐chemical calculations. Calculations of the UV spectrum showed that the photodecomposition is induced by an n→σ* transition, but the nature of the excitation differs when different light sources are used. There is strong evidence for the formation of mobile ¹D excited O atoms in the case of excitation at 365 nm, which led to the formation of (η²‐O₂)XeO₃ by reaction with XeO₄. Matrix‐isolation IR spectroscopy in Ne and Ar matrices afforded the natural‐abundance xenon isotopic pattern for the ν₃(T₂) stretching mode of Xe¹⁶O₄, and ¹⁸O enrichment provided the ¹⁶O/¹⁸O isotopic shifts of XeO₄ and (η²‐O₂)XeO₃.