Properties of ThFx from Infrared Spectra in Solid Argon and Neon with Supporting Electronic Structure and Thermochemical Calculations
Kanchana Thanthiriwatte, Xuefeng Wang, Lester Andrews, David Dixon, Jens Metzger, Thomas Vent-Schmidt, Sebastian Riedel – 2014
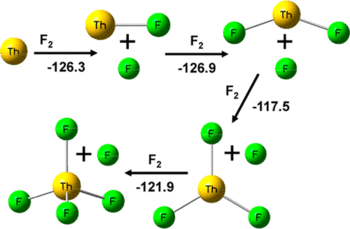
Laser-ablated Th atoms react with F₂ in condensing noble gases to give ThF₄ as the major product. Weaker higher frequency infrared absorptions at 567.2, 564.8 (576.1, 573.8) cm⁻¹, 575.1 (582.7) cm⁻¹ and 531.0, (537.4) cm⁻¹ in solid argon (neon) are assigned to the ThF, ThF₂ and ThF₃ molecules based on annealing and photolysis behavior and agreement with CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ vibrational frequency calculations. Bands at 528.4 cm⁻¹ and 460 cm⁻¹ with higher fluorine concentrations are assigned to the penta-coordinated species (ThF₃)(F₂) and ThF₅⁻. These bands shift to 544.2 and 464 cm⁻¹ in solid neon. The ThF₅ molecule has the (ThF₃)(F₂) Cs structure and is essentially the unique [ThF₃⁺][F₂⁻] ion pair based on charge and spin density calculations. Electron capture by (ThF₃)(F₂) forms the trigonal bipyramidal ThF₅⁻anion in a highly exothermic process. Extensive structure and frequency calculations were also done for thorium oxyfluorides and Th₂F₄,₆,₈ dimer species. The calculations provide the ionization potentials, electron affinities, fluoride affinities, Th–F bond dissociation energies, and the energies to bind F₂ and F₂⁻ to a cluster as well as dimerization energies.