Glycan-Induced Transchelation of Gadolinium from Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent-Complexes
Polewski, L.; Dymnikova, D.; Malicka, W.; Lettow, M.; von Helden, G.; Teutloff, C.; Ballauff, M.; Taupitz, M.; Bittl, R.; Pagel, K.* – 2025
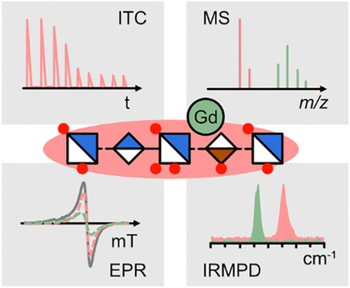
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear, highly acidic polysaccharides that serve as essential extracellular matrix components. There has been increasing evidence that GAGs can release gadolinium ions from complexes of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. This unintended release of gadolinium might be an initial step leading to gadolinium deposition disease, as observed in some patients after intravenous injection of such contrast agents. However, the molecular details of the release remain poorly understood. In this work, we provide direct evidence for gadolinium binding by GAGs using synthetic model substance Fondaparinux (FPX), a heparin mimetic. We observed FPX–gadolinium complexes in mass spectrometry experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) and characterized the binding by EPR, isothermal titration calorimetry, and gas-phase infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Finally, we were able to follow the transchelation process on a molecular level by utilizing collision-induced dissociation experiments.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear, highly acidic polysaccharides that serve as essential extracellular matrix components. There has been increasing evidence that GAGs can release gadolinium ions from complexes of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. This unintended release of gadolinium might be an initial step leading to gadolinium deposition disease, as observed in some patients after intravenous injection of such contrast agents. However, the molecular details of the release remain poorly understood. In this work, we provide direct evidence for gadolinium binding by GAGs using synthetic model substance Fondaparinux (FPX), a heparin mimetic. We observed FPX–gadolinium complexes in mass spectrometry experiments and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR) and characterized the binding by EPR, isothermal titration calorimetry, and gas-phase infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Finally, we were able to follow the transchelation process on a molecular level by utilizing collision-induced dissociation experiments.