Fine-Tuning the Proteolytic Stability of Peptides with Fluorinated Amino Acids
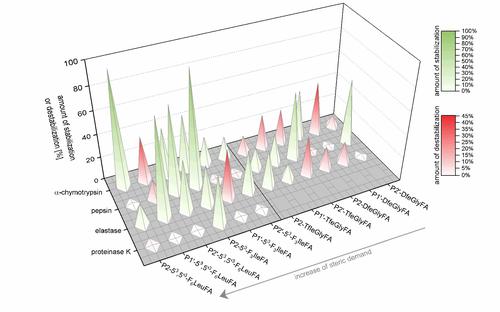
Rapid hydrolysis by proteases of the blood or digestive system usually limits the application of peptides as therapeutics. To systematically investigate the influence of fluorinated amino acids on the proteolytic stability of peptides, we synthesized a model peptide library that contained amino acids with systematically changed fluorine content at different positions relative to the protease cleavage sites. Using an analytical reversed phase HPLC assay with fluorescence detection and mass-spectrometric experiments, the proteolytic stability of the peptides was characterized.
The studies show that the impact of incorporation of side-chain fluorinated amino acids on the proteolytic stability is not predictable and cannot be generalized. Depending on the substitution position relative to the cleavage site, the chemical nature and fluorine content of the side chain, and the particular protease, fluorine substituents can alter the resistance of peptides towards proteolytic digestion in various ways. Sterically demanding, and/or highly fluorinated amino acids such as 53,5’3-F6Leu or 53-F3Ile seem to be more efficient in inducing protease resistance, but our experiments reveal that also amino acids with a smaller side chain (TfeGly and DfeGly) are able to significantly improve proteolytic stability in cases where highly fluorinated analogues clearly fail.
Our results provide valuable knowledge for the design of stable peptide-based drugs and contribute to the evolution of fluorination as a powerful tool in peptide and protein engineering.
Further Reading
S. Huhmann, B. Koksch, Fine-Tuning the Proteolytic Stability of Peptides with Fluorinated Amino Acids. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 3667-3679. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201800803
S. Huhmann, A.-K. Stegemann, K. Folmert, D. Klemczak, J. Moschner, M. Kube, B. Koksch, Position-dependent impact of hexafluoroleucine and trifluoroisoleucine on protease digestion. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2869-2882. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.13.279
V. Asante, J. Mortier, G. Wolber, B. Koksch, Impact of fluorination on proteolytic stability of peptides: a case study with α-chymotrypsin and pepsin. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2733-2744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1819-7
V. Asante, J. Mortier, H. Schlüter, B. Koksch, Impact of fluorination on proteolytic stability of peptides in human blood plasma. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3542-3546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.03.051